Cannabis & Music
"Music combined with cannabis tends to produce feelings of euphoria and connectedness to the music and the musicians." - Daniel Levitin, professor of neuroscience at McGill University
Cannabis enhances present focus and inhibits searching through the memory so it it allows you to focus on and be captivated by the music!
Cannabis vs Alcohol
ALCOHOL
Many people have died from the health effects of alcohol
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that more than 30,000 annual U.S. deaths are attributed to the health effects of alcohol not including accidental deaths.
People die from alcohol overdoses
The official publication of the Scientific Research Society, American Scientist, reported that alcohol is one of the most toxic drugs and using just 10 times what one would use to get the desired effect could lead to death.
The CDC attributes more than 1,600 U.S. deaths per year to alcohol poisoning.
CANNABIS
Nobody has died from the health effects of Cannabis
The CDC does not have a category for deaths caused by the health effects of cannabis. A study published in Scientific Reports in January 2015 found that the mortality risk associated with marijuana was approximately 114 times less than that of alcohol.
There has never been a fatal cannabis overdose
Cannabis is one of the least toxic drugs, theoretically requiring thousands of times the dose one would use to get the desired effect to lead to death.
Cannabis & Harm Reduction
Cannabis as a Substitute
Sample included 2,841 respondents of which the majority (91%) used non-prescribed cannabis & more than half (54.6%) had used cannabis with the purpose of replacing a prescribed drug.The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that more than 30,000 annual U.S. deaths are attributed to the health effects of alcohol not including accidental deaths.
Compared to non-substitution users, substitution users were...
- More likely to be women
- More likely to use CaM in the treatment of chronic pain and other somatic conditions
- Pain medication (67.2%)
- Antidepressants (24.5%)
- Arthritis medication (20.7%)
- 38.1% reported termination of prescription drug use
- 45.9% reported a substantial decrease in prescription drug use.
- CBD-oil (65.2%)
- Skunk, pot, hash- (36.6%)
- 65.8% found cannabis to be much more effective compared to prescription drugs
- 85.5% found that the side effects associated with prescription drug use were much worse compared to use of canabis
Physiology
The Endocannabinoid System
Involved in crucial physiological processes including- Nervous system development, immune function, inflammation, appetite, metabolism and energy, homeostasis, cardiovascular function, digestion, bone development and bone density, synaptic plasticity and learning, pain, reproduction, psychiatric disease, psychomotor behavior, memory, wake/sleep cycles, and the regulation of stress and emotional state/mood
Serrano A, Parsons LH, Pharmacol Ther, 2011
McPartland JM, Matias I, Di Marzo V, Gene. 2006
McPartland, John M, . The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association, American Osteopathic Association, 2008
THC & CBD
THC Effects & Benefits
- Psychoactive
- Relieves of pain, inflammation, PTSD, Migraines, insomnia, GI symptoms, spasticity, nausea, anxiety, and stimulates appetite
- Enhances mood, uplifting
- Stimulates euphoria and alters perception
- Relaxing and sedating
Cascio MG, Pertwee RG. Handbook of cannabis., 2015
CBD Effects & Benefits
- Non-psychoactive,non-impairing
- Shown to calm the mind, relieve anxiety, depression, pain, seizures, psychosis, inflammation, spasm, and nausea
- Can regulate THC to make it more manageable
Russo, E., Mead, A., & Sulak, D, Clinical Researcher, 2015
Zuardi, Antonio Waldo, Revista brasileira de psiquiatria, 2008
Types of Cannabis
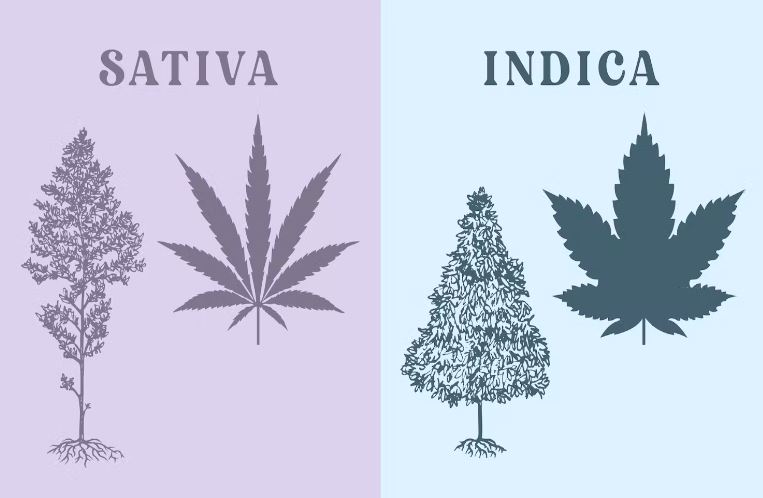
Sativas
Typically thought to be energizing, sativas originally grew in warm, humid climates, growing long and lanky so they can dry out and not absorb so much humidity. Their warm climate also means they can take a long time to grow and flower, or produce buds, because the weather won’t get cold and rainy at the end of the growing season.
Indicas
Typically said to be relaxing, indicas originally grew in cold, northern climates. They grew short and dense because of their environment, and their growing life cycle is shorter so they can get harvested before the cold and wet of fall and winter set in.
Hybrids
Typically have a mix of indica and sativa effects.
LeaflyTerpenes
Common Terpenes in Cannabis
 Russo, Ethan B. "Taming THC: potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid‐terpenoid entourage effects." British journal of pharmacology 163.7 (2011): 1344-1364.
Russo, Ethan B. "Taming THC: potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid‐terpenoid entourage effects." British journal of pharmacology 163.7 (2011): 1344-1364.
Therapeutic Effects of Terpenes
- The fragrance and flavor of cannabis are determined by the terpenes in a particular strain.
- Good strains for daytime are usually low in the sedating terpenes myrcene, linalool, and nerolidol, and have higher levels of pinene and limonene.
- Good strains for evening are myrcene and linalool.
- Often those with anxiety with anxiety, pain, and muscle spasticity may prefer such strains, even for daytime use, due to superior therapeutic effects for their conditions.
- People with depression may benefit from strains dominant in limonene and pinene, and avoiding the more sedating strains of cannabis.
- People that struggle with short-term memory side effects of cannabis may do best with strains high in a-pinene.
Sulak, Dustin DO. “Be A Trusted Cannabis Advisor.” Medical Cannabis Core Curriculum, training.healer.com/.
Forms of Cannabis
Sample Cannabis Products

Ways to Consume Cannabis
Inhalation
- Heat activates the THC and CBD (de-carboxalation)
- Vaporization (plant or concentrate)
- Smoking
- Quick maximal effect, short duration effect
- 1-5 min onset
- Duration 1-6 hours - Tapers off within 2-3 hours
Sulak, Dustin DO. “Be A Trusted Cannabis Advisor.” Medical Cannabis Core Curriculum, training.healer.com/
Oral
- Edibles, beverages
- Cannabinoids are lipid soluble so they are easily absorbed in the small intestine.
- Slower, longer duration effect that inhalation
- Onset 30 -120 minutes
- Duration 4-12 hours
Topical
- Oil-based extracts can be added to balms, lotions, salves, patches, and liniments.
- Can be applied topically to help alleviate pain, muscle spasms, inflammation, itching, and various skin conditions, including eczema.
- Topical use of cannabis typically does not produce psychoactive effects unless used in high potencies over large surface areas of skin. Both THC and CBD have therapeutic properties when used topically.
- Topical products labeled “transdermal,” such as patches, are designed for better absorption and will have a full-body effect
Sublingual/Oral Mucosal
- Absorbed through the mucous membrane in the mouth
- Onset 10-45 Minutes
- Duration 2-8 Hours
Cannabis Dosing
Broad Dosing Range
Cannabis dosing is highly individualized and relies largely on slowly increasing dose. Start low and go slow.Response to cannabis depends on...
- Genetic differences in cannabinoid receptor structure and function
- Individual differences in cannabinoid metabolism affecting cannabinoid bioavailability
- Prior exposure to and experience with cannabis/cannabinoids
- Changes to cannabinoid receptor distribution/density and/or function as a consequence of a medical disorder
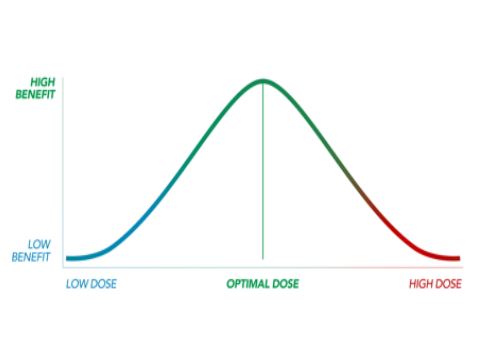
Optimal Dose
Evidence from a clinical study suggests a dose-dependent, bi-phasic, effect of THC on anxiety and mood:
- Low doses of THC appear to have an anti-anxiety and mood-elevating effect
- High doses of THC can produce anxiety and lower mood
MacCallum, Caroline A, and Ethan B Russo, European Journal of Internal Medicine, 2018
Rey, Alejandro Aparisi, et al, Neuropsychopharmacology, 2012
Sulak, Dustin DO. “Be A Trusted Cannabis Advisor.” Medical Cannabis Core Curriculum, training.healer.com/
Overconsumption
Recognizing Overconsumption
- Increased paranoia, anxiety, and/or panic attacks
- Increased heart rate
- Difficulty walking or picking up objects
- Involuntary eye movement or twitching
- Slurred speech
- Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome: stomach cramping with repeated and severe bouts of vomiting (very rare)
Responding to Overconsumption
The effects of overconsumption can often be alleviated by- Reassuring the affected individual
- Allowing them to rest in a comfortable environment
- Providing water and other fluids for rehydration
- Administer Chillax Cannabis Calming Formula or a comparable amino acid product that counteracts the effects of cannabis consumption.